
April 8, 2025 | 6:00 pm
Table of Contents
How powerful would it be to use financial forecasting to glimpse into your business’s
future? Despite its significant benefits, many SMEs still overlook this essential practice.
This oversight often traps them in a cycle of reactive decision-making, where they
constantly put out fires instead of preventing them.
Fortunately, it’s never too late for business owners to break free and take a more proactive
approach to their finances. Financial forecasting lets you see what lies ahead in your
business, make smarter business decisions, manage risks, and secure a better financial
future.
Read on to take control of your business’s financial destiny. Start prioritizing your
financial forecasting today and set your business to sustainable success.
Why is financial forecasting important?
In today's volatile market, SMEs can't afford to act blindly.
Financial forecasting provides the clarity needed to understand the market's complexities
and anticipate future challenges. It’s the difference between reactive scrambling and
proactive success.
Here are five compelling reasons why you cannot afford to ignore financial forecasting:

Smarter business decisions
Financial forecasting, when rooted in data, directly enables smarter business decisions. By
analyzing historical trends and real-time data, you gain a clearer picture of your financial
future.
This data-driven approach is particularly crucial for making sound financial decisions for
small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Operating with smaller financial cushions than
larger corporations, SMEs cannot afford to rely on guesswork.
SMEs can use financial forecasting to anticipate challenges and opportunities. For example,
a forecast can help predict a company's slow sales period and allow the business to adjust
its expenses or secure funding in advance.
On the other hand, if the business sees an opportunity to expand, it can use forecasting to
check whether it can afford to spend on growth initiatives like hiring more people before
actually executing the plan.
Enhanced cash flow management
Effective financial forecasting helps SMEs enhance their cash flow management.
Using forecasts, entrepreneurs can quickly see whether the company will have low or high
liquidity periods. Awareness of these scenarios can help improve budgeting, ensure
sufficient funds for all financial obligations, and reduce the risk of cash shortages.
Forecasts also help create cash flow benchmarks that entrepreneurs can use to track whether
they earn enough revenue to cover their expenses.
For example, SMEs can compare actual and forecasted cash flow to determine whether they need
to adjust their spending, improve how they collect payments, or refine their payment
schedule.
If you want to learn more about how to improve your cash flow aside from using financial
forecasts, check out this video:
Risk reduction and mitigation
Financial forecasting is an effective way to reduce and mitigate risks in business.
Forecasts help small businesses identify possible risks, allowing them to plan ahead and
avoid problems.
While a forecast can’t wholly predict every business risk or challenge, it can still help
minimize its impact, improve recovery time, and assist SMEs in weathering tough times.
Access to financing
If you want to grow your business, you may need to raise capital through bank loans or
investors. Nevertheless, having a financial forecast handy will significantly enhance your
ability to secure financing.
Financial forecasts promote transparency and build trust with potential financiers, making
it easier to obtain their approval.
When seeking funding, lenders and investors often require businesses to present detailed
forecasts to determine whether the company can generate enough revenue to pay off its loans
or provide a return on investment.
Similarly, SMEs can review their forecasts before applying for loans to determine if they
can afford the additional debt and how future repayments will impact their cash flow. By
factoring in both the borrowed amount and repayment obligations, forecasts can show if the
business can still cover its costs without financial strain.
Appeal to investors
Like businesses, investors use forecasts to make choices. With a forecast, investors clearly
see the company’s future performance and growth potential.
Investors are bombarded with pitches and plans daily, so to make your business stand out,
you must present a compelling forecast showing how additional funding will drive growth and
deliver a strong return on investment.
Moreover, financial forecasting attests to your ability to control the business, manage
risks, and plan strategically for the company’s future.
How is financial forecasting done?
Financial forecasting is a tool for
predicting a company’s future financial performance by
analyzing historical data, market trends, and prevailing economic conditions.
Here are some valuable tips to help build a robust financial forecast for your SME:
What are the key components of financial forecasting?

A comprehensive financial forecast mainly needs a cash flow projection, a profit and loss
projection, and a balance sheet. These documents are similar to SMEs' financial reports,
except they cover the future and not the past.
Besides these pro forma documents, SMEs can also consider additional factors to make their
forecasts more reliable.
Here are the different components of a financial forecast:
Cash flow projection
A cash flow projection assesses liquidity by projecting changes in the company’s cash balance. With this document, SMEs can anticipate periods of shortages and surpluses and plan accordingly.
Profit and loss projection
This document compares your expected revenue against anticipated expenses to determine whether profits or losses will occur within the forecasting period. This projection determines whether business strategies are viable or sustainable in the long term.
Balance sheet forecasting
This component reports the company’s estimated assets, liabilities, and equities. For example, increased inventory or additional equipment can boost assets, while future loan repayments or increased accounts payable impact your liabilities.
Risk analysis
When forecasting, SMEs need to identify potential risks to the business and create plans to mitigate or avoid them. These risks could be internal, like employee turnover, or external, such as economic downturns.
Scenario planning
Forecasts should also consider the best-case and worst-case scenarios in the business to determine how these can impact your finances. Some examples of scenarios to consider are a sudden surge in market demand or disruptions in the supply chain.
Two methods of financial forecasting
The methods of financial forecasting can generally be divided into two groups: quantitative
forecasting and qualitative forecasting.
When choosing a forecasting method, businesses should consider how much historical data they
can use. Companies with rich historical data can use quantitative methods since they
require
extensive data or numbers to produce accurate forecasts.
Meanwhile, businesses with little to no data can use qualitative methods as an alternative
while they don’t have enough records yet.
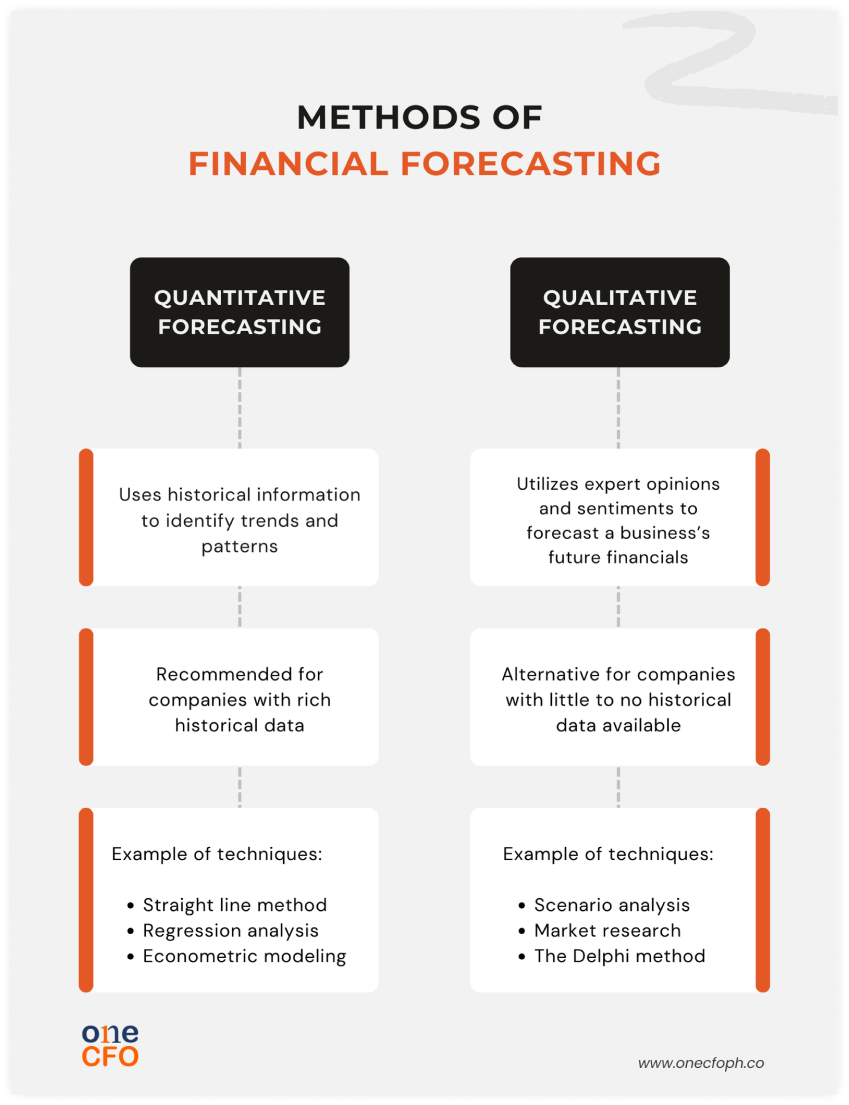
Quantitative forecasting
This method of forecasting uses historical information to identify trends and patterns.
Businesses typically find this historical data in their financial statements, which include
income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
Here are some of the common quantitative techniques in forecasting:
Qualitative forecasting
Qualitative forecasting methods can be a good alternative for businesses with insufficient
historical data to estimate your company’s financial health. The techniques used in the
qualitative method mainly use experts' opinions or sentiments to analyze the company and the
market.
Qualitative forecasting techniques include the following:
How often should you update your financial forecast?
Maintaining an accurate and reliable financial forecast is crucial for informed
decision-making in the dynamic world of finance. As market conditions, consumer behaviors,
and business operations evolve, so too should your forecasts.
But how frequently should these updates occur?
This question does not have a straightforward answer, as it mainly depends on your
business’s needs and objectives.
Entrepreneurs should also understand the trade-off between granularity and frequency when
forecasting.
Essentially, the more granular or detailed the forecast is, the less frequently it can be
updated, and vice versa. Highly specific forecasts require more time and resources to
prepare, limiting the ability to update them frequently.
Businesses in high-growth and volatile industries may find it more beneficial to obtain
frequent forecast updates but with moderate granularity.
On the other hand, more stable businesses can afford to have more detailed annual forecasts
with periodic reviews.
What’s the difference between forecasting and budgeting?
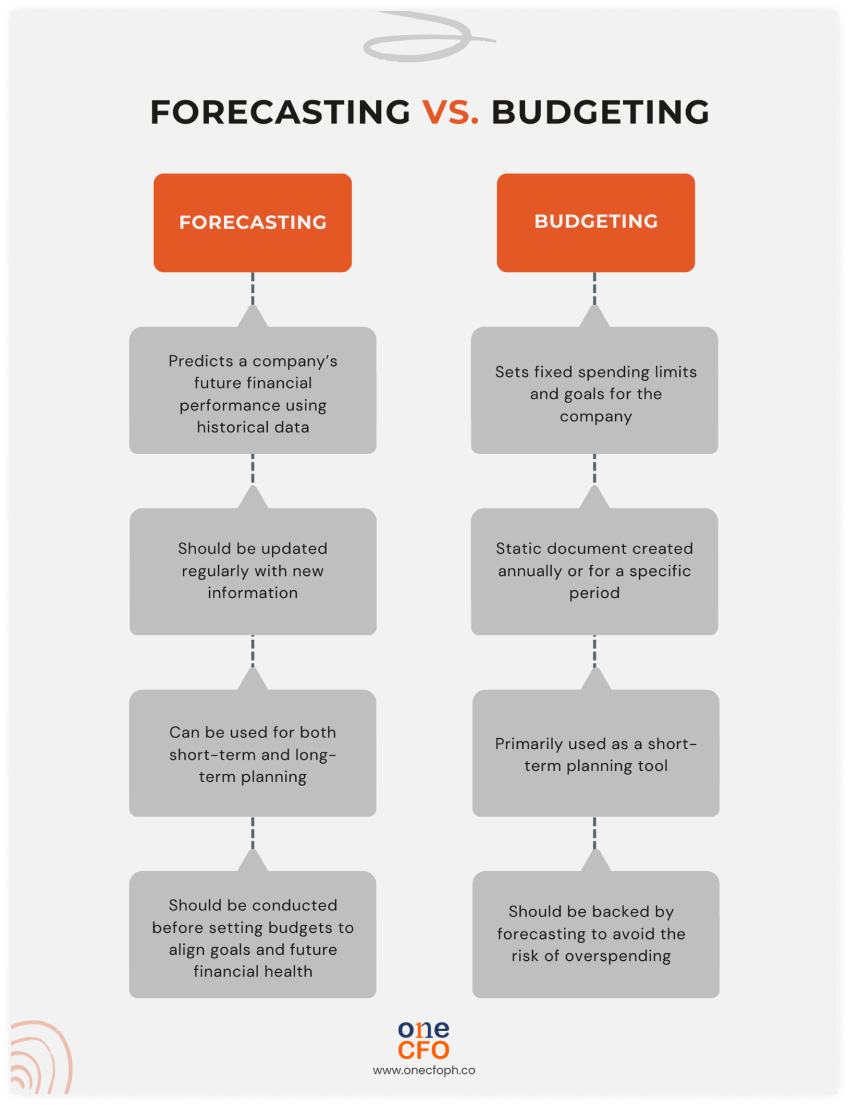
A common misconception in business finance is that forecasting and budgeting mean the same
thing. These two processes are distinct, each crucial for sound financial planning.
Forecasting is the process of predicting a company’s future financial performance using
historical data, which can be updated regularly as you gather new data. Ideally, this
process should come before budgeting to ensure that your spending goals are aligned with the
company’s future financial performance.
On the other hand, budgeting involves setting fixed
spending limits or goals based on
expected revenue and expenses for a specific period. Simply put, budgeting is where
entrepreneurs decide how to allocate resources.
Without a forecast to guide budgeting, businesses risk overspending or being unprepared for
emergencies.
Join others who are already mastering their finances with this invaluable video guide on
budgeting:
Secure your business’ future with solid financial forecasts
Are you letting your competitors race ahead while you navigate financial blind spots?
Every day you delay solid financial forecasting is a day you risk missing out on crucial
growth opportunities. SMEs that leverage data-driven forecasts are the ones securing their
future, not just surviving.
Don't let limited expertise hold you back. OneCFO provides the fractional CFO expertise you
need in building financial forecasts that transform uncertainty into strategic advantage.
Imagine the confidence of making decisions with absolute clarity. Stop guessing and start
growing.
Visit us at onecfoph.co or email us at [email protected]
before it's too late - your future depends on it.
Read our disclaimer here.